Java에서는 Executor을 통해서 Thread Pool을 직접 구현하지 않고 사용할 수 있다.
+) 참조 : Thread Pool 설명이 잘 되어 있는 블로그 글 : https://hamait.tistory.com/612
Executor Service
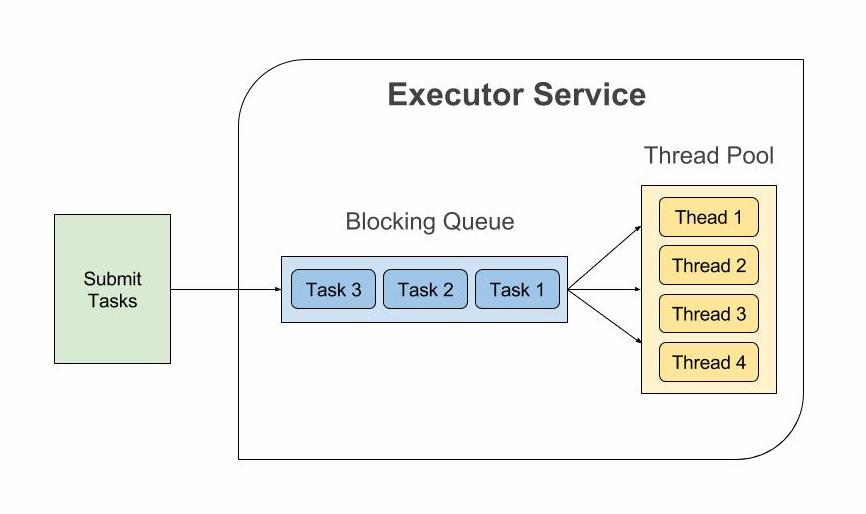
- 작업 Queue + 재사용 위해 준비된 Thread들 (Thread Pool)
Executor 사용법
1. Executors 클래스를 통해 ExecutorService를 생성
// 2개의 Thread를 가지는 Thread Pool을 가지고 있는 ExecutorService 생성
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
-
CachedThreadPool,FixedThreadPool,ScheduledThreadPool,SingleThreadExecutor… 등과 같은 다양한ExecutorService가 있다.
+) 참조 : https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/Executors.html
2. Thread를 작업 Queue에 제출
-
execute메소드service.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } });// 람다식 service.execute(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }); -
submit메소드service.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } });// 람다식 service.submit(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); });
💡 execute, submit 어떤 차이일까?
| execute | submit | |
|---|---|---|
| 메소드 | Executor.execute(Runnable command) | ExecutorService.submit(Callable |
| ExecutorService.submit(Runnable task, T result) | ||
| ExecutorService.submit(Runnable task) | ||
| 리턴 값 | O | O / X |
| Exception 발생시 | Thread 종료 후 재생성 | Thread 재사용 |
- 인자
-
execute:Runnable -
submit:Callable,Runnable
-
- 리턴값 유무
Runnable실행시 리턴 값이 없고,Callable실행시Future형태의 리턴 값을 받을 수 있다. (실행 Thread의 결과 값을 받을 수 있다.)-
execute: 리턴 값 X -
submit: 리턴 값 O / X
-
- Exception
-
execute실행 중 Exception이 발생하는 경우- 해당 Thread는 stacktrace 출력 후 종료
- 다음 Task 작업시 Thread Pool에는 새로운 Thread 생성
-
submit실행 중 Exception이 발생하는 경우- 해당 Thread는 종료되지 않고 재사용
-
submit메소드로 리턴되는Future의get메소드를 호출시 Exception이 리턴됨 - 즉,
submit메소드를 통해서 호출된 Thread는 Exception이 발생하더라도Future.get()을 호출하지 않는다면 Exception의 stacktrace는 출력되지 않음
- 예제코드: Code Example 3
-
Executor 구조 (feat. class diagram)
-
newFixedThreadPool메소드를 호출하면ThreadPoolExecutor인스턴스를 리턴public class Executors { public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); } ... } -
ThreadPoolExecutor클래스는AbstractExecutorService를 상속public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService { ... } -
AbstractExecutorService클래스는ExecutorService를 구현public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService { ... } -
ExecutorService인터페이스는Executor를 상속public interface ExecutorService extends Executor { ... } -
Executor인터페이스public interface Executor { void execute(Runnable command); }
Executor Class diagram
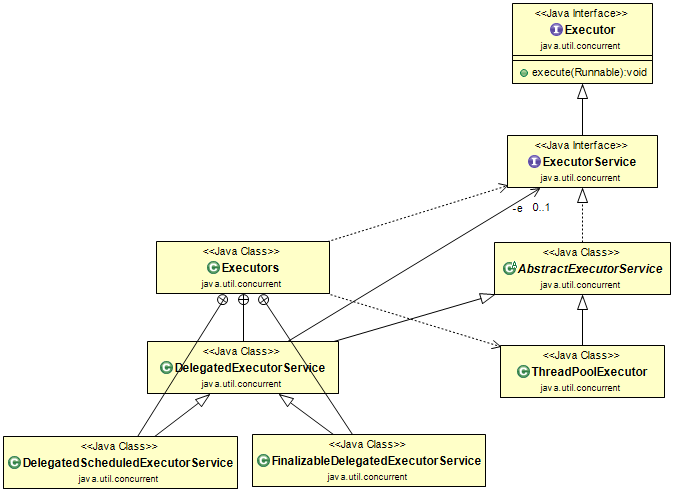
-
Executors클래스를 통해 생성된ExecutorServie들은Executor의execute메소드,ExecutorService의submit메소드를 구현하여 사용함
Code Example
Code Example 1 - (return 없음)
-
FixedThreadPool을 사용하여 3개의 ThreadPool 생성 - 10개의 Task를
execute - 각 Task는 3초의 시간 소요
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void testFixedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testFixedThreadPool();
}
}
결과
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-3
----------------------------------
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-1
- thread1, thread2, thread3이 3초마다 출력되는 것을 확인
Code Example 2 - (return 있음)
-
SingleThreadExecutor을 사용하여 1개의 ThreadPool 생성 - 작업의 결과를 리턴받음 (
true)
public class ExecutorTest {
public static Future<Boolean> testSingleThreadExecutor() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
return service.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return true;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Future<Boolean> result = testSingleThreadExecutor();
System.out.println("RESULT : " + result.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
결과
pool-1-thread-1
RESULT : true
- 결과 값을 리턴받음을 확인
Code Example 3 - (execute, submit Exception 비교)
(1) execute
- Code Example 1 코드에서
RuntimeException발생만 추가
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void testFixedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException(); // 추가
});
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testFixedThreadPool();
}
}
결과
pool-1-thread-1
----------------------------------
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-2
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-3"
pool-1-thread-4
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-2" java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-1" java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
pool-1-thread-6
pool-1-thread-5
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-5"
pool-1-thread-7
java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-6"
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-4" java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
pool-1-thread-8
pool-1-thread-9
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-7" java.lang.RuntimeException
pool-1-thread-10
at ...
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-8" java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-9" java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-10" java.lang.RuntimeException
at ...
- 순서가 좀 섞여서 나오지만 thread들이 재사용 되지 않고 재생성됨을 확인
(2) submit
- Code Example 1 코드에서
execute->sumbit수정,RuntimeException발생 추가
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void testFixedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
service.submit(() -> { // 수정
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException(); // 추가
});
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testFixedThreadPool();
}
}
결과
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-2
----------------------------------
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-3
- thread 재사용하는 것을 확인
-
Future.get()호출하지 않음으로 Exception의 stacktrace가 출력되지 않음을 확인
+) 참조 :
https://hamait.tistory.com/612
https://codechacha.com/ko/java-executors/
https://www.callicoder.com/java-executor-service-and-thread-pool-tutorial/